The recently released Report on Status of Devolution to Panchayats in India: An Indicative Evidence Based Ranking, 2024, published by the Ministry of Panchayati Raj, underscores India’s transformative journey towards maximum governance and empowered local institutions. The report highlights the progress made in decentralization and the crucial role of Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs) in shaping a self-reliant and inclusive Naya Bharat, aligning with Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s vision for Viksit Bharat by 2047.
Historical Foundations: Key Amendments and Milestones
India’s journey towards decentralization has been shaped by several constitutional amendments and historical events that laid the foundation for strengthening PRIs. The 73rd Constitutional Amendment Act (1992) institutionalized the Panchayati Raj system by providing constitutional status to PRIs. It mandated the creation of three-tier local governance—Gram Panchayat, Block Panchayat, and District Panchayat with regular elections, financial devolution, and decision-making authority.
Similarly, the 74th Constitutional Amendment Act (1992) strengthened urban local bodies, ensuring the decentralization of governance in municipal corporations and municipalities. Several committees have played a pivotal role in shaping local governance structures, including the Balwant Rai Mehta Committee (1957), which recommended the three-tier system of Panchayati Raj, and the Ashok Mehta Committee (1978), which proposed a two-tier system and emphasized direct elections and financial autonomy for Panchayats.
The G.V.K. Rao Committee (1985) and L.M. Singhvi Committee (1986) stressed the need for empowering Panchayats by granting them constitutional status, leading to the eventual passage of the 73rd and 74th Amendments. Over the years, various Finance Commissions have continuously recommended direct devolution of funds to PRIs, ensuring their financial stability and sustainability.
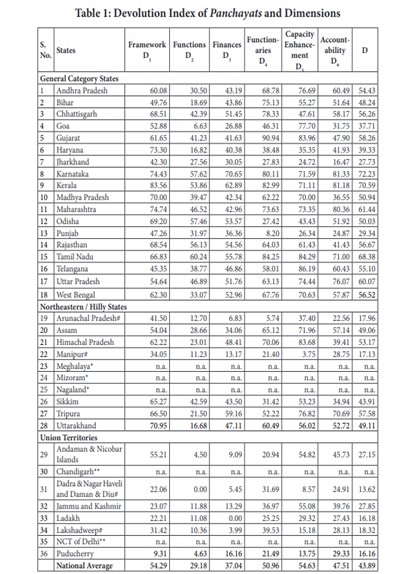
Key Findings of the Report on Status of Devolution to Panchayats in India, 2024
The Report on Status of Devolution to Panchayats in India, 2024 evaluates states based on six dimensions:
| Dimension | Description |
| Framework | Legal and institutional structures for PRIs. |
| Functions | Transfer of responsibilities to PRIs. |
| Finances | Financial autonomy and fund flow mechanisms. |
| Functionaries | Administrative capacity and staffing. |
| Capacity Building | Training programs for PRI representatives. |
| Accountability | Transparency, social audits, and governance mechanisms. |
According to the report, Karnataka secured the top rank (72.23), followed by Kerala (70.59) and Tamil Nadu (68.38). Notably, Uttar Pradesh (BJP-ruled) made a significant leap from 15th place to 5th, demonstrating the impact of governance reforms under Naya Bharat’s vision. Additionally, states like Gujarat, Rajasthan, and Madhya Pradesh also showed strong performance, proving that decentralization efforts are yielding tangible results.
PM Modi’s Vision of Naya Bharat and Maximum Governance
Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s vision for Naya Bharat is anchored in the principle of Sabka Saath, Sabka Vikas, Sabka Vishwas, and Sabka Prayas. This vision places emphasis on people’s participation (Jan Bhagidari), transparency, and maximum governance to drive holistic development across urban and rural areas alike.
Under initiatives such as Gram Swaraj Abhiyan and Aatmanirbhar Bharat, PRIs have been placed at the center of local governance. PM Modi believes in strengthening self-sustaining villages through direct financial empowerment, technological integration, and community-driven decision-making.
Transformative Reforms Strengthening Local Governance
Several key reforms have been instrumental in improving India’s governance framework at the grassroots level:
- Direct Fund Transfers: The government has ensured that funds are transferred directly to Panchayats under the 15th Finance Commission, minimizing bureaucratic delays and ensuring efficient utilization.
- Digital Transformation: The implementation of e-Panchayat platforms, digital property tax collection, and online grievance redressal systems has enhanced transparency and service efficiency at the local level.
- Capacity Building Programs: Training initiatives such as Rashtriya Gram Swaraj Abhiyan (RGSA) are equipping local leaders with essential governance skills.
- Financial Independence for PRIs: Many states have strengthened financial devolution, enabling Panchayats to generate revenue through local taxation, service charges, and public-private partnerships (PPPs).
- Infrastructure Development: Programs such as Jal Jeevan Mission, PM Awas Yojana (Gramin), and Swachh Bharat Mission (Rural) have significantly improved rural infrastructure and service delivery.
A Continuous Assessment Process for Viksit Bharat 2047
This ongoing process of evaluating devolution serves as a crucial tool for achieving PM Modi’s vision of Viksit Bharat by 2047. By maintaining a constant cycle of assessment, reform, and implementation, India is steadily moving towards a governance model of minimum government and maximum governance. This approach ensures that decision-making is efficient, decentralized, and driven by local needs, empowering citizens and local leaders as active participants in nation-building.
Way Ahead: Strengthening Naya Bharat’s Governance Model
The Report on Status of Devolution to Panchayats in India, 2024 is a stepping stone in India’s larger vision of becoming a developed nation by 2047. To further enhance decentralization and governance efficiency, several key actions need to be taken:
- Strengthening institutional frameworks to ensure timely elections and effective devolution of powers.
- Expanding technology-driven governance to enhance transparency and efficiency at all levels.
- Enhancing the autonomy of PRIs to foster local-level innovation and decision-making.
- Providing incentives for best-performing Panchayats to encourage innovation in local governance.
The Report on Status of Devolution to Panchayats in India, 2024 highlights India’s commitment to strengthening local governance as a critical pillar of Naya Bharat. As the nation progresses towards Amrit Kaal, the emphasis on local governance and self-reliance will be instrumental in shaping India’s future. The findings of this report underscore that effective decentralization is not just about governance—it is about empowering people to build the New India together.
(The views expressed are the author's own and do not necessarily reflect the position of the organisation)

